Sampling and Inference Fundementals
Lecture 8
NC State University
ST 511 - Fall 2025
2025-09-15
Checklist
– HW-1 grades are released
> email Nick and I if you have any questions– HW-2 released today (due Sunday at 11:59pm)
> your repo is called homework-2
> we will look at the number of commits you have– Quiz released Wednesday (due Sunday at 11:59pm)
– I wrote up a resource on random variables / probability distributions on our website! Check it out.
Warm-up
What do we mean by population?
What do we mean by sample?
Warm-up
Population - “complete set”, or every possible observational unit of interest
Sample - a subset of data collected from a larger population
Warm-up
What’s a ranodm sample?
Why do we care?
Warm-up
Random sample - subgroup of observational units selected from a larger population where every unit has an equal chance of being chosen
– Helps ensure observations are independent
– Helps ensure observations are representitative of the larger population
Warm-up
What’s the difference between a probability distribution and a sampling distribution?
Warm-up
A probability distribution describes the set of all possible values a random variable can take and the probability of each value occurring
A sampling distribution is essentially the probability distribution of a statistic (like the sample mean or sample proportion) from all possible samples of a given size.
Goals for Today
– More with random variables, probability distributions, and sampling distributions
– Sampling schemes
– Inference (Hypothesis Testing)
Example
Let X = the number of minutes a college student plays video games in a week. Assume that X is distributed normal with a mean of 60 and a standard deviation of 20.
– What does 60 mean? What does 20 mean?
– How do we write mathematically how X is distributed?
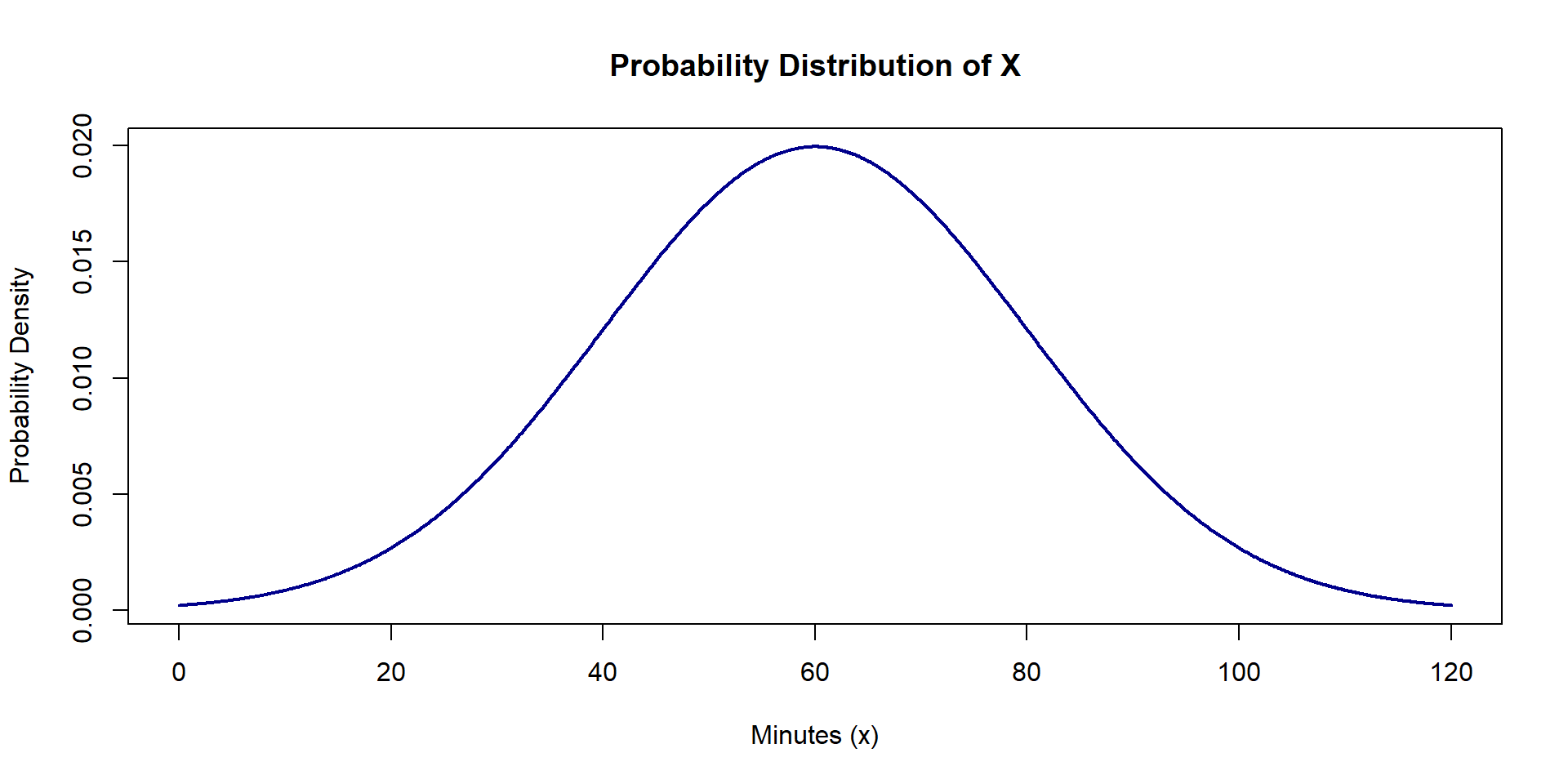
Example
What probability are we calculating? How can we write this out in mathematical notation?
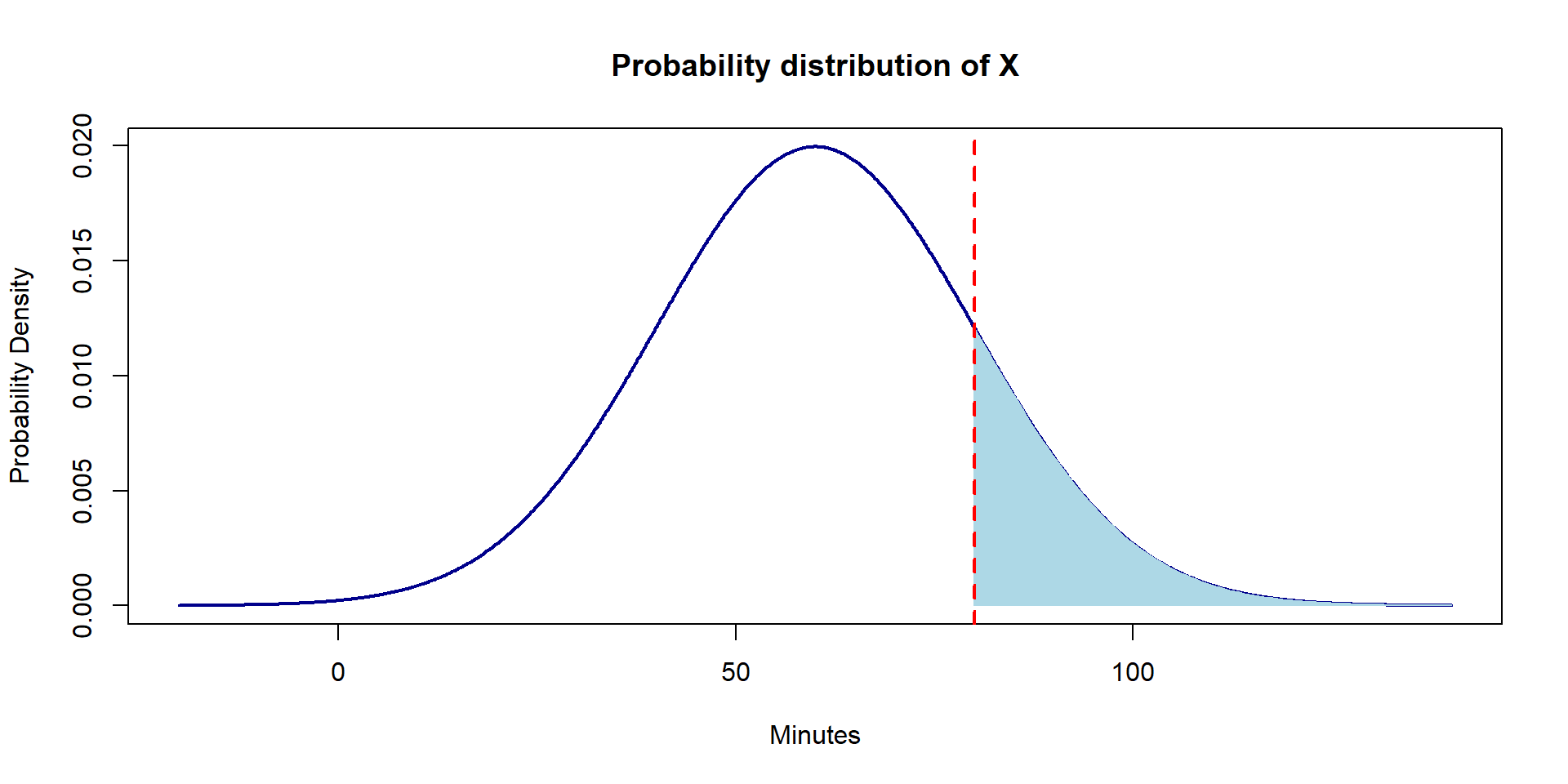
Questions?
Sampling
Gettysburg Address (3-minutes)
– Pick 10 random words
– Take the mean
– Report it
Sampling
Let’s talk about different sampling schemes
– Simple random sample
– Systematic sampling
– Convinence sampling
(more complex techniqeus later)
Random sample
Advantages
– Helps us assume independence
– Helps us generalize to a larger population
Disadvantages
– It’s really hard… could be difficult to actually target a truly large population of interest
Sampling Schemes
– Random sampling ✔️
– Systematic sampling
– Convinence sampling
Systematic sampling
A probability sampling technique where you select participants from a larger population by choosing a random starting point and then selecting every nth individual from a list or sampling frame
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
– Helps us assume independence
– Helps us generalize to a larger population
Disadvantages
– Risks bias if the population has a hidden periodic pattern
– Need to know your entire sampling frame
Types of sampling
– Random sampling ✔️
– Systematic sampling ✔️
– Convinence sampling
Convenience sampling
Convenience sampling: a non-random sampling method where participants are selected based on their availability, willingness, or ease of access
Can be useful in certain situations (observational studies)… but
– non-representative
– sampling bias can occur
Questions
Hypothesis Testing
Set up a null and alternative hypothesis (let’s talk about this)
Collect data
Check assumptions
Analyze data
Make decisions and conclusions
Context
We are going to test to see if a coin is fair!
Let’s collect data
Assumptions
For our hypothesis test, we need to check the following assumptions:
– Independence (do we satisfy this condition?)
– Normality
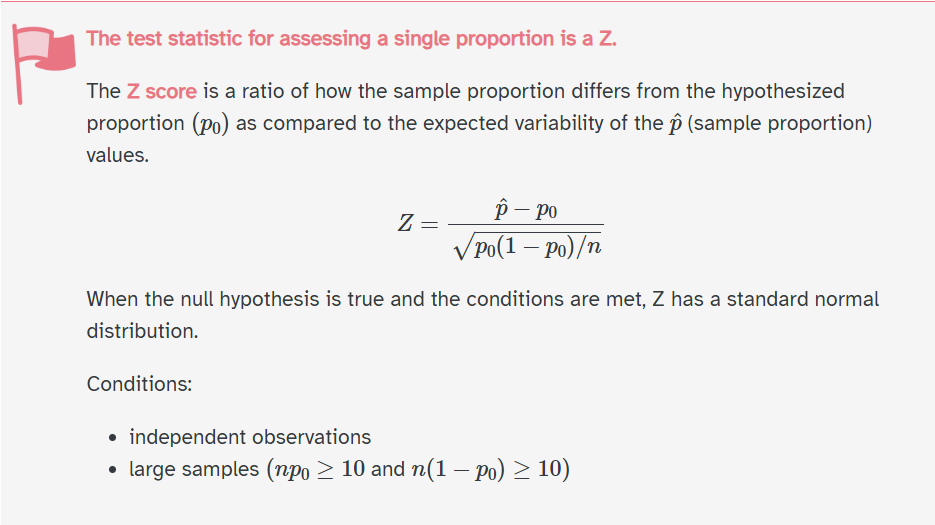
Normality
– n* \(\pi_o\) > 10
– n* (1 - \(\pi_o\)) > 10
Do we satisfy this condition?
Sampling Distribution of p-hat
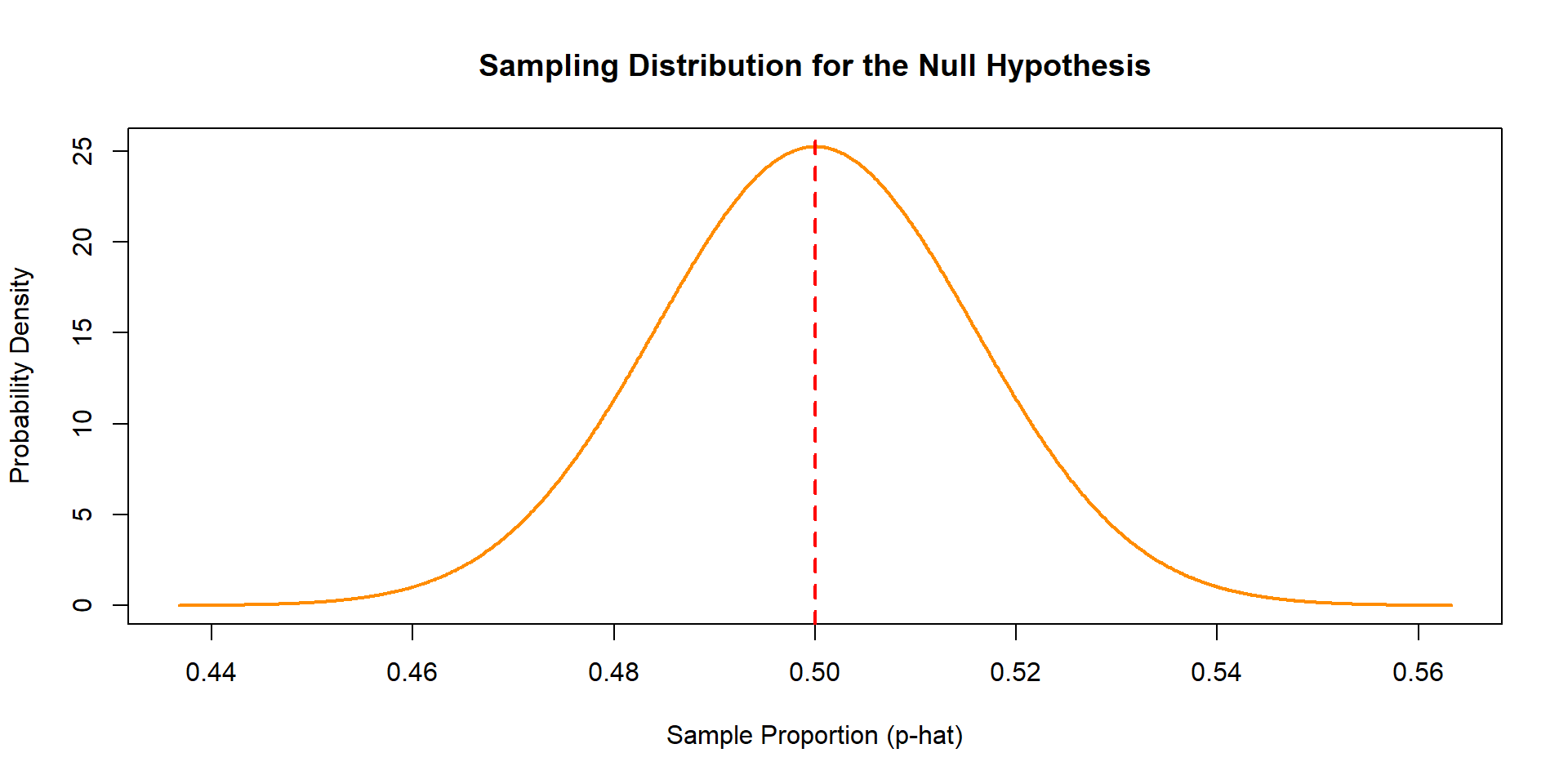
What is the standard error of the sampling distribution?
Note: The standard deviation of the sampling distribution is called the standard error!
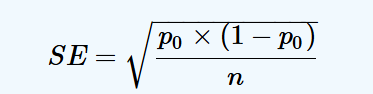
p-value
Replace test_stat, null_mean, ect with the appropriate values
Z-distribution
Decisions and Conclusions
– Decisions are always in terms of the null
– Conclusions are always in terms of the alternative
Typically, researchers use fixed level testing \(\alpha\).
What is \(\alpha\)?
