GitHub + Quarto + R Intro
Lecture 2
NC State University
ST 511 - Fall 2025
2025-08-20
Checklist
– Did you read the prepare material?
– Did you make a GitHub account?
– Can you access R + RStudio?
Announcements
We will start in-class activities (AEs) today. This will be the primary mode of learning throughout the semester. These will not be turned in for a grade. This means that they are entirely for you.
The weekly quizzes (starting next week) will be a check-in to see if you are completing the AEs
Use these activities to build yourself notes/resources to reference both during and after the semester!
Goals for today
– Introduce R+RStudio, GitHub, and Quarto
– Understand why we are learning these tools
– Link together RStudio and GitHub
– Understand the file structure of a New Project in RStudio
– Introduce the flow of GitHub
– RStudio tour
Warm Up 1: Types of Variables
Categorical or Quantitative?
– Height
– Weight
– Zip Code
– Coffee Drinker(Low, Med, High)
Warm Up 1: Types of Variables
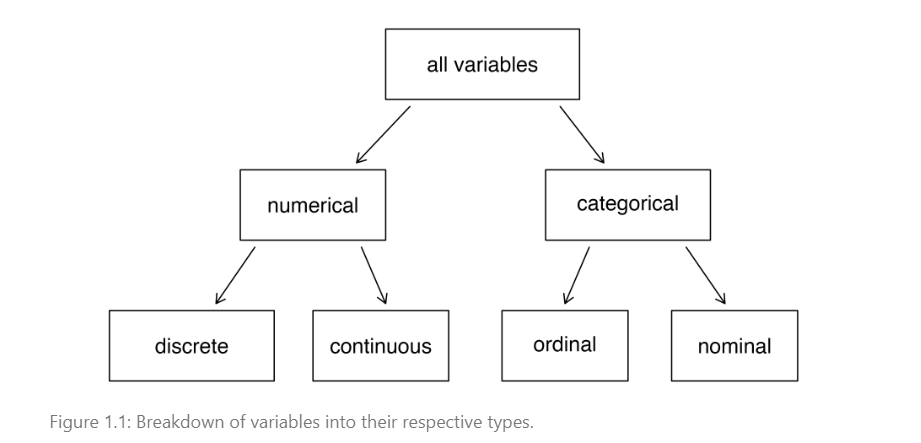
Warm Up 1: Types of Variables
Categorical
> ordinal: category of data that can be ordered
> nominal: category of data with no inherent order
Quantitative
> discrete: takes on countable values
> continuous: takes on any value within a range (including decimals)Warm Up 2: Variables
– Explanatory Variable
– Response Variable
Warm Up 2: Variables
From the text: When we suspect one variable might causally; predict; influence change in another we label the first variable the explanatory variable and the second the response variable
Warm Up 3: Types of Studies
– Observational Study
– Experiment
Warm Up 3: Types of Studies
Researchers perform an observational study when they collect data in a way that does not directly interfere with how the data arise.
In an experiment, we often manipulate; control; fix; administer the explanatory variable.
Questions?
What is R and RStudio?
– R is a statistical programming language
– RStudio is a convenient interface for R

R-layout
Some R essentials
– Functions are (normally) verbs, followed by what they will be applied to in parentheses:

R essentials
Packages are installed with the install.packages function and loaded with the library function, once per session:

Packages
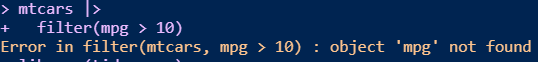
library(tidyverse)
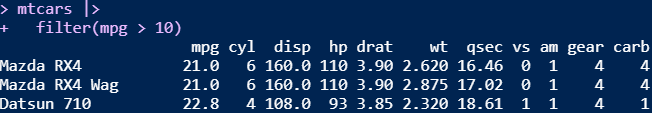
Packages
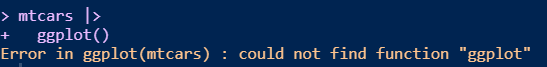
library(tidyverse)

tidyverse

– The tidyverse is a collection of R packages designed for data science.
– All packages share an underlying philosophy and a common grammar.
Git and GitHub
Often used interchangably, but it’s nice to know the difference…
Git is a version control system that intelligently tracks changes in files.
GitHub is a cloud-based platform where you can store, share, and work together with others to write code.
Think of this as email (Git) vs Gmail (GitHub)
GitHub: Version control
GitHub allows you to create, store, change, merge, and collaborate on files or code. Any member of a team can access the GitHub repository and see the most recent version in real-time. Then, they can make edits or changes that the other collaborators also see.
GitHub also lets users make requests of one another and internally discuss the iterations along the way.
GitHub: Version control
Demo
I’m going to Demo how we use RStudio and GitHub together (motivate)
Then, we will walk through the steps for you to link up RStudio and GitHub
(If time) We will talk about Quarto + Demo the proper GitHub workflow
Demo
Linking RStudio and GitHub
These directions are in the ae_sa column in our schedule. You can find that here.
We will go through these directions together
Where AEs are located
Moodle! I’ll show you!
Clone an AE
What does cloning mean?
What is the process of cloning a GitHub repo?
Let’s demonstrate!
Demo AE
GitHub WorkFlow
GitHub Commands: Pull Commit Push
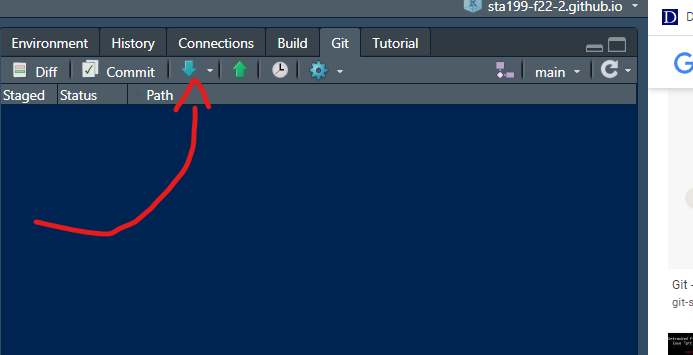
GitHub Commands: Pull Commit Push
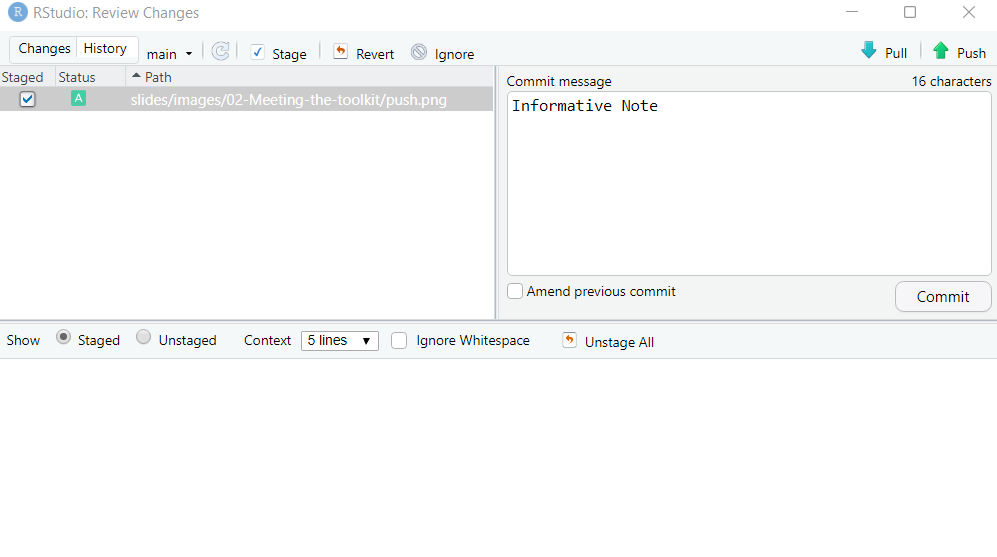
GitHub Commands: Pull Commit Push
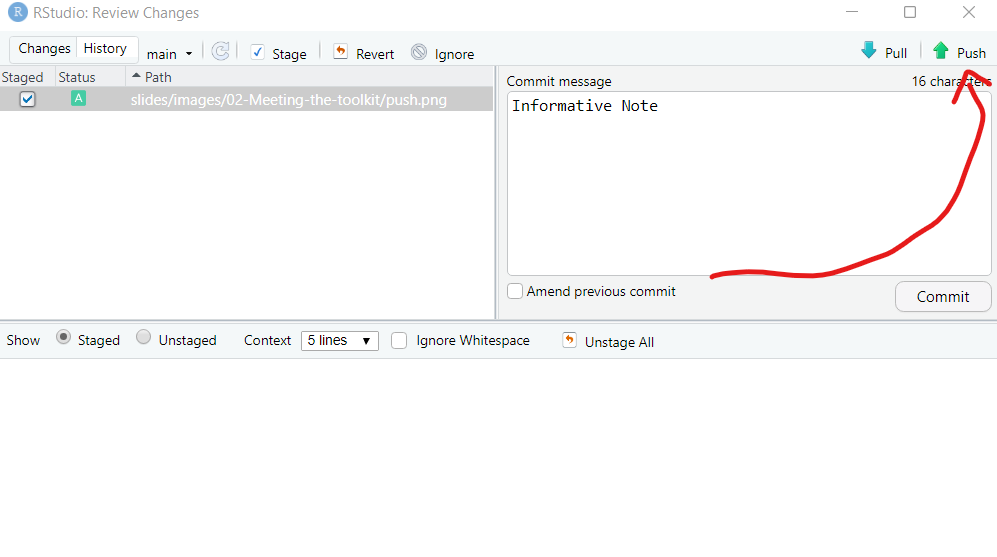
Quarto
– an open-source scientific and technical publishing system
– publish high-quality articles, reports, presentations, websites, blogs, and books in HTML, PDF, MS Word, ePub, and more
– Code goes in chunks, defined by three backticks, narrative goes outside of chunks
How will we use Quarto?
– Every assignment / lab / project will be given to you as a Quarto document
– You will always have a Quarto template document to start with
– As we get more familiar with R, the more code you will construct on your own
How to make PDFs (if time)
To be able to compile PDFs, you will also need to download TinyTex. You can do so by running the following code in your Console.
tinytex::install_tinytex()Note: If you are on a Mac, you already have this!
Wrap up
– What is version control? Why is it important?
– What is R vs RStudio?
– What is a R package?
